nft
本文最后更新于:2023年12月5日 晚上
相关文档:
- https://wiki.nftables.org/wiki-nftables/index.php/Main_Page
- https://wiki.nftables.org/wiki-nftables/index.php/Nftables_families
man nft
nftables 和 iptables 一样,依赖的底层机制都是 Netfilter,但是 nftables 各个方面都比 iptables 更优秀,未来一定会成为主流,所以有必要好好学习。
升级 nftables
CentOS8 自带的 nftables 版本是 0.9.3,而官网最新的版本是 0.9.6,所以需要先升级:
卸载系统自带的 nftables
[root@centos8 src]$yum remove nftables.x86_64 [root@centos8 src]$rpm -qa | grep ntf [root@centos8 src]$去官网下载最新版本
# 官网:http://netfilter.org/projects/nftables/downloads.html [root@centos8 ~]$cd /usr/local/src/ [root@centos8 src]$yum -y install bzip2 [root@centos8 src]$tar jxvf nftables-0.9.6.tar.bz2 [root@centos8 src]$ll total 844 drwxr-xr-x. 10 lujinkai lujinkai 4096 Jun 15 16:24 nftables-0.9.6 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 859481 Sep 27 06:49 nftables-0.9.6.tar.bz2安装
[root@centos8 src]$cd nftables-0.9.6/ [root@centos8 nftables-0.9.6]$ [root@centos8 nftables-0.9.6]$mkdir /usr/local/nftables [root@centos8 src]$yum -y install gcc [root@centos8 nftables-0.9.6]$./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nftables ... # 报错,缺少libmnl依赖 checking for LIBMNL... no configure: error: Package requirements (libmnl >= 1.0.4) were not met: .... # 安装libmnl参考:https://centos.pkgs.org/8/centos-baseos-x86_64/libmnl-1.0.4-6.el8.x86_64.rpm.html [root@centos8 nftables-0.9.6]$dnf install libmnl # 安装libmnl-devel参考:https://centos.pkgs.org/8/centos-powertools-x86_64/libmnl-devel-1.0.4-6.el8.x86_64.rpm.html [root@centos8 nftables-0.9.6]$dnf --enablerepo=PowerTools install libmnl-devel [root@centos8 nftables-0.9.6]$ldconfig [root@centos8 nftables-0.9.6]$./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nftables ... # 报错,缺少libnftnl依赖 checking for LIBNFTNL... no configure: error: Package requirements (libnftnl >= 1.1.7) were not met: No package 'libnftnl' found Consider adjusting the PKG_CONFIG_PATH environment variable if you installed software in a non-standard prefix. Alternatively, you may set the environment variables LIBNFTNL_CFLAGS and LIBNFTNL_LIBS to avoid the need to call pkg-config. See the pkg-config man page for more details. ... # 上面的libmnl通过dnf安装,这个libnftnl就通过编译安装吧,从nftables官网下载最新的libnftnl源码包 [root@centos8 nftables-0.9.6]$cd .. [root@centos8 src]$tar jxvf libnftnl-1.1.7.tar.bz2 [root@centos8 src]$cd libnftnl-1.1.7/ [root@centos8 libnftnl-1.1.7]$./configure --prefix=/usr/local/libnftnl-1.1.7 [root@centos8 libnftnl-1.1.7]$make && make install ... # 根据提示,要指定libnftnl的lib和include,这个要查看具体的pkg-config文件 # vim /usr/local/libnftnl-1.1.7/lib/pkgconfig/libnftnl.pc # ... # 15 Libs: -L${libdir} -lnftnl # 16 Cflags: -I${includedir} [root@centos8 nftables-0.9.6]$(LIBNFTNL_CFLAGS=-I/usr/local/libnftnl-1.1.7/include/ LIBNFTNL_LIBS="-L/usr/local/libnftnl-1.1.7/lib/ -lnftnl" ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nftables) ... # 报错,缺少libgmb依赖 checking for __gmpz_init in -lgmp... no configure: error: No suitable version of libgmp found [root@centos8 nftables-0.9.6]$yum -y install gmp gmp-devel # 继续 [root@centos8 nftables-0.9.6]$./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nftables ... # 缺少 libreadline 依赖 checking for readline in -lreadline... no configure: error: No suitable version of libreadline found [root@centos8 nftables-0.9.6]$dnf -y install readline readline-devel [root@centos8 nftables-0.9.6]$./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nftables # 安装成功 nft configuration: cli support: readline enable debugging symbols: yes use mini-gmp: no enable man page: yes libxtables support: no json output support: no enable Python: no配置 systemctl
[root@centos8 ~]$vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/nftables.service # 从另一台机器上拷贝一份yum安装自动生成的nftables.service文件,稍作改动 [Unit] Description=Netfilter Tables Documentation=man:nft(8) Wants=network-pre.target Before=network-pre.target [Service] Type=oneshot ProtectSystem=full ProtectHome=true ExecStart=/usr/local/nftables/sbin/nft -f /usr/local/nftables/etc/nftables/all-in-one.nft ExecReload=/usr/local/nftables/sbin/nft 'flush ruleset; include "/usr/local/nftables/etc/nftables/all-in-one.nft";' ExecStop=/usr/local/nftables/sbin/nft flush ruleset RemainAfterExit=yes [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target # 设置开机自启 [root@centos8 ~]$systemctl enable --now nftables.service配置环境变量
# 将 /usr/local/nftables/sbin 添加到PATH(位于/etc/profile) export PATH=/usr/local/nftables/sbin:/usr/local/nginx/sbin:$PATH # 重载 . /etc/profile
nftables 和 iptables 的区别
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
nf和 xt
nf是 netfilter 的缩写,nf_ 前缀的模块是 netfilter 的核心模块(以下称 nf 模块),nftables 之前,netfilter 提供了 iptables、ip6tables、arptables 等用户空间工具,xtables 就是这些工具的统称,缩写为 xt。可能是为了便于理解或者什么理由,专为 xtables 开发的模块以 xt前缀命名(以下称 xt 模块),当然,xtables 也可以调用 nf 模块。
安装 iptables 后,会生成/usr/lib64/xtables/目录,目录下就是各种 xt 模块。
xtables 既能调用 xt 模块,也能调用 nf 模块,为了方便我们把 xt 模块和 nf 模块统称为扩展。
现在,这些 xtables 工具被认为是过时的,推荐使用 nftables,nftables 是 xtables 的全面替代品,nftables 调用的都是 nf 模块,所以安装后自然也不会生成 /usr/lib64/xtables/目录。
因为并没有找到参考资料,以上都是个人理解和猜测,说的不一定准确。
表(Tables)
与 iptables 类似,在 nftables 中,表是链的容器,nftables 不包含任何的表和链,所以开始使用 nftables 时,首先需要添加至少一个表,然后向表里添加链,然后往链里添加规则。
地址簇与钩子函数
什么是地址族?
地址族:又叫地址簇,AF,Address;不要太纠结这个名称,可以认为就是 地址类型。
另外,还有协议族:又叫协议簇,PF,Protocol Family;协议族等价于地址族。
netfilter 中六个勾子函数(hook),前面 iptables 章节一节已经介绍过了,这里再说一遍,六个钩子函数是:
INGRESS、PREROUTING、INPUT、OUTPUT、FORWARD、POSTROUTING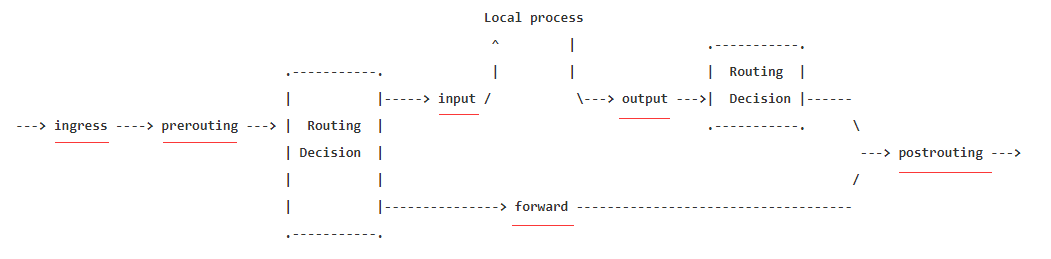
添加表
语法:
nft {add | create} table [<family>] <table>family:表支持的地址类型,有六种,每个表只能指定一种,默认是 ip,表示 IPv4
family 表示的地址族 iptables 中对应的命令行工具 ip IPv4 地址 iptables ip6 IPv6 地址 ip6tables inet IPv4 和 IPv6 地址 iptables 和 ip6tables arp 地址解析协议(ARP)地址 arptables bridge 处理桥接数据包 ebtables netdev 内核 4.2 之后可用。只能使用 ingress 钩子,在路由之前进行过滤,可以替代 tc命令
范例:
# 添加一个 IPv4 的 foo 表
nft add table ip foo
# 添加一个 IPv6 的 bar 表
nft add table ip6 bar列出表
# 列出所有表
[root@centos8 ~]$nft list tables
table ip foo
table ip6 bar
# 列出一个或多个地址族的所有表,注意这时是tables
[root@centos8 ~]$nft list tables ip
table ip foo
# 列出一个表中的所有链
[root@centos8 ~]$nft list table ip foo
table ip foo { # 目前表中还没链
}删除表
[root@centos8 ~]$nft delete table ip6 bar说明:内核 3.18 以前,需要先清空表中的内容,再删除表
清空表
# 清空表中所有链中的所有规则
[root@centos8 ~]$nft flush table ip foo链(Chains)
ntfables 没有内置的链,所有的链都需要手动创建,链有两种类型:基本类型和常规类型。
其中基本类型又分类三类:filter、nat、route
基本链:base chains,数据包的入口,需要指定钩子函数和优先级,类似 iptables 中的内置链
type 表 钩子函数 描述 filter all all 过滤 nat ip、ip6、inet prerouting、input、output、postrouting 地址转换,第一个包总是命中这个链,因此不要用此链进行过滤 route ip、ip6 output 策略路由选择器,等价于 iptables 中的 mangle 表,但是仅用于 output 钩子函数 常规链:regular chains,不需要指定钩子函数和优先级,可以用来做跳转,从逻辑上对规则进行分类,类似 iptables 中的自定义类
创建链
语法:
# 创建常规链
nft add chain [<family>] <table> <chain>
# 创建基本链
nft add chain [<family>] <table> <chain> {type <type> hook <hook> [device <device>] priority <priority>; [policy <policy>;] }type:可以选择 filter、nat、route
hook:钩子函数,六个钩子函数,只能指定一个,不同的表 family 支持不同的钩子函数:
family hook ip、ip6、inet prerouting、input、forward、output、postrouting arp input、output bridge prerouting、input、forward、output、postrouting netdev ingress 小总结:netdev 只支持 ingress + filter 一种组合;arp 支持 { input | output } + filter 两种组合
device:netdev 表只存在于每个传入接口,所以它需要指定 device 参数
priority:优先级,可以接受 整数值 或者 标准优先级名。整数值可以为负,数值越低优先级越高;有以下数值可以选择
- NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_DEFRAG (-400): priority of defragmentation
- NF_IP_PRI_RAW (-300): traditional priority of the raw table placed before connection tracking operation
- NF_IP_PRI_SELINUX_FIRST (-225): SELinux operations
- NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK (-200): Connection tracking operations
- NF_IP_PRI_MANGLE (-150): mangle operation
- NF_IP_PRI_NAT_DST (-100): destination NAT
- NF_IP_PRI_FILTER (0): filtering operation, the filter table
- NF_IP_PRI_SECURITY (50): Place of security table where secmark can be set for example
- NF_IP_PRI_NAT_SRC (100): source NAT
- NF_IP_PRI_SELINUX_LAST (225): SELinux at packet exit
- NF_IP_PRI_CONNTRACK_HELPER (300): connection tracking at exit
policy:链的策略,支持的策略值是 accept、drop,默认是 accept
范例:
# 添加常规链
[root@centos8 ~]$nft add chain ip foo chain_1
# 添加基本链
[root@centos8 ~]$nft add chain ip foo chain_2 {type filter hook input priority 0\;}列出链
# 列出一个表中的所有链
[root@centos8 ~]$nft list table ip foo
table ip foo {
chain chain_1 {
}
chain chain_2 {
type filter hook input priority filter; policy accept;
}
}
# 列出一个链中的所有规则
[root@centos8 ~]$nft list chain ip foo chain_1
table ip foo {
chain chain_1 { # 目前链中还没有规则
}
}
[root@centos8 ~]$nft list chain ip foo chain_2
table ip foo {
chain chain_2 { # 目前链中还没有规则
type filter hook input priority filter; policy accept;
}
}编辑链
把添加链语法的 add 或者 create 关键字去掉,就是编辑链的语法
# 编辑常规链
nft chain [<family>] <table> <chain>
# 编辑基本链
nft chain [<family>] <table> <chain> {[type <type> hook <hook> [device <device>] priority <priority> ; [policy policy ;]] }范例:
# 将chain_1链策略从accept更改为drop
nft chain ip foo chain_1 { policy drop \; }删除链
要删除的链不能包含任何规则或者跳转目标。
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]$nft delete chain ip foo chain_1
[root@centos8 ~]$nft list table ip foo
table ip foo {
chain chain_2 {
type filter hook input priority filter; policy accept;
}
}清空链
范例:
# 清空chain_2链中的所有规则
[root@centos8 ~]$nft flush chain ip foo chain_2规则(Rules)
iptables 和 nftables 的区别
参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/dog250/article/details/41526421?locationNum=8
iptables
iptables 是由表、链、规则组成,其中规则又由 match、target 组成。
iptables 的规则是按照配置顺序顺序匹配的,在每一张表的每一个链上依次匹配每一条规则,在每一条规则依次匹配每一个 match,全部匹配的 match 执行该规则的 target,由 target 决定:
- 继续匹配下一条规则
- 对数据包做一些修改
- 跳转到其它的链(即开始从该链依次匹配该链上的每一条规则)
- 返回引发跳转的链(即继续匹配跳转前的链的下一条规则)
- 丢弃数据包
- 接收数据包(即不再继续往下匹配,直接返回)
- 记录日志
- …
整个 iptables 框架的执行流程如下:
循环1:
static breakrule = 0;
遍历一个chain的每一条rule {
nomatch = 0;
循环2:遍历一条rule的每一个match {
result = rule->match[curr](skb, info);
if(result != MATCH) {
nomatch = 1;
break;
}
}
if (nomatch == 1) {
continue该chain的下一条rule;
}
result = rule->target(skb, info);
if (result == DROP) {
break丢弃数据包
} else if (result == ACCEPT) {
break接受数据包
} else if (result == GOTO) {
breakrule = rule;
跳转到相应的chain,执行循环1
} else if (result == RETURN) {
break返回调用chain,执行其breakrule的下一条rule
} ...
}可以发现,包过滤的流程最终要落实到规则匹配,而过滤的动作最终落实到了该规则的 target,前面的所有的 match 匹配返回结果就是 0 或者非 0 表示是否匹配,只有所有的 match 均匹配,才会执行 target。这也就导致了如果你想实现多个 target,就不得不写多条规则。
nftables
nftables 的规则去掉了“匹配所有的 match 之后执行一个 target”这样的限制,使一条规则真的成了“为一个数据包做一些事情”这样灵活的命令。我们来看一下 nftables 框架的执行流程:
循环1:
static breakrule = 0;
遍历一个chain的每一条rule {
nomatch = 0;
reg[MAX]
循环2:遍历一条rule的每一个expression {
void rule->expression[curr]->operations->expr(skb, info, reg)
if(reg[VERDICT] != CONTINUE) {
break;
}
}
if (reg[VERDICT] == CONTINUE) {
continue该chain的下一条rule;
} else if (reg[VERDICT] == DROP) {
break丢弃数据包
} else if (reg[VERDICT] == ACCEPT) {
break接受数据包
} else if (reg[VERDICT] == GOTO) {
breakrule = rule;
跳转到相应的chain,执行循环1
} else if (reg[VERDICT] == RETURN) {
break调用chain,执行其breakrule的下一条rule
} ...
}可以看到,nftables 没有 match 和 target,而是将一条 rule 抽象成了若干条的表达式,即 expression,所谓的表达式就是一个主语加谓词的式子,它是“可执行”的,它可以“做任何事情”,而不仅仅是计算一个匹配结果。除此之外,nftables 内置了一组寄存器,其中之一是 verdict 寄存器,它指示了“下一步要怎么做”。每一条 expression 执行完了之后,会取出该寄存器,由该寄存器的值来采取下一步的行动。这个 verdict 寄存器替换了 iptables 中 target 返回值,这就可以在一条 rule 中采取多个动作,每条动作可以解析成一个 expression,只要每一个 expression 在执行后将 verdict 寄存器设置为 CONTINUE 即可。
除了执行流程的显著区别之外,nftables 最大的意义在于它对 expression 进行了抽象,nftables 的内核框架可以注册很多种的 expression,其中 expr 回调函数执行具体的 expression 表达式。
表达式 expression
规则由表达式组成,表达式有匹配表达式,和动作表达式两种,但官方文档不是这么划分的,而是分成表达式和语句,其实表达式就是匹配表达式,语句就是动作表达式,下文如果没有特别说明,采用的是官方的说法。
例如规则:
ip saddr 10.1.1.1 tcp dport ssh accept就是由ip sadd、tcp dpor两条表达式和accept一条语句组成
每个表达式都有一个数据类型
describe
describe 命令可以显示表达式 或 数据类型的信息
语法:
# 列出表达式的信息
describe <expression>
# 列出数据类型的信息
describe <datatype>范例:
# describe <expression>
[root@centos8 ~]$nft describe ct state
ct expression, datatype ct_state (conntrack state) (basetype bitmask, integer), 32 bits
pre-defined symbolic constants (in hexadecimal):
invalid 0x00000001
new 0x00000008
established 0x00000002
related 0x00000004
untracked 0x00000040
# describe <datatype>
[root@centos8 ~]$nft describe ct_state
datatype ct_state (conntrack state) (basetype bitmask, integer), 32 bits
pre-defined symbolic constants (in hexadecimal):
invalid 0x00000001
new 0x00000008
established 0x00000002
related 0x00000004
untracked 0x00000040
# describe <expression>
[root@centos8 ~]$nft describe tcp dport
payload expression, datatype inet_service (internet network service) (basetype integer), 16 bits
# describe <datatype>
[root@centos8 ~]$nft describe inet_service
datatype inet_service (internet network service) (basetype integer), 16 bitsdatatype
数据类型分级别,全局数据类型是最低阶的,有 integer、string 两种,高阶的数据类型从低阶的派生而来,例如:bitmask 从 integer 派生而来,ct_state 从 bitmask 派生而来。
大部分数据类型固定长度,少部分不固定。
一些高阶的数据类型具有预定义的符号常量,例如:boolean 类型,固定 size 1bit,取值 0 或 1,预定义了 exists 和 missing 两个字符常量,会被自动替换为 1 和 0;
- integer:用于数值,可以指定为十进制、十六进制或八进制,没有固定大小
- string:用于字符串,以字母开头,此外,双引号内的任何内容都被认为是字符串
- bitmask:用于位掩码,基于 integer,至于什么是位掩码,自行百度或参考文章:什么是掩码 BitMask
- boolean:用于布尔值,固定 size 1bit
- inet_service:用于服务端口,固定 size 16bit
- ipv4_addr:用于 IPv4 地址,固定 size 32bit,预定义字符常量 localhost
- icmp_type:用于 ICMP 类型,固定 size 8bit,取值 0-18,预定义了 echo-reply、echo-request 等 19 个字符常量,会被自动替换为 0-18
- 链接跟踪
- ct_state
- ct_status
- …
- …
expression
分为主表达式和有效负载表达式,不知道有什么区别,看起来好像在一条规则中,主表达式的位置在有效负载表达式的前面。
以下是对所有表达式做一个全面但简略的记录,详细信息参考:https://jlk.fjfi.cvut.cz/arch/manpages/man/nft.8
PRIMARY EXPRESSIONS
-
meta 就是数据包的元数据,元表达式有限定和非限定两种,限定不能省略 meta 关键字,非限定则可以省略
# mete 关键字不可省略 meta {length | nfproto | l4proto | protocol | priority} # meta 关键字可以省略 [meta] {mark | iif | iifname | iiftype | oif | oifname | oiftype | skuid | skgid | nftrace | rtclassid | ibrname | obrname | pkttype | cpu | iifgroup | oifgroup | cgroup | random | ipsec | iifkind | oifkind | time | hour | day }范例:
[root@centos8 ~]$nft describe meta iif meta expression, datatype iface_index (network interface index) (basetype integer), 32 bits [root@centos8 ~]$nft describe meta oif meta expression, datatype iface_index (network interface index) (basetype integer), 32 bits [root@centos8 ~]$nft describe meta iifname meta expression, datatype ifname (network interface name) (basetype string), 16 characters -
套接字表达式用于搜索已打开的 TCP/UDP 套接字,及其与数据包关联的属性
socket {transparent | mark} -
被动操作系统指纹识别。此表达式将数据包中的某些数据(窗口大小、MSS、选项及其顺序、DF 等)与 SYN 位集进行比较
osf [ttl {loose | skip}] {name | version}- ttl:对包进行 TTL 检查以确定操作系统
- version:对包进行 OS 版本检查
- name:要匹配的操作系统签名的名称。所有的签名都可以在 pf.os 文件中找到。对表达式无法检测到的操作系统签名使用“unknown”
-
fib {saddr | daddr | mark | iif | oif} [. ...] {oif | oifname | type} -
路由表达式指的是与数据包关联的路由数据
rt [ip | ip6] {classid | nexthop | mtu | ipsec} -
ipsec {in | out} [ spnum NUM ] {reqid | spi} ipsec {in | out} [ spnum NUM ] {ip | ip6} {saddr | daddr} -
numgen {inc | random} mod NUM [ offset NUM ] -
使用一个哈希函数来生成一个数字。可用的函数是 jhash(Jenkins 散列)和 symhash(对称散列)。
jhash 和 symhash 的典型用例是负载均衡jhash {ip saddr | ip6 daddr | tcp dport | udp sport | ether saddr} [. ...] mod NUM [ seed NUM ] [ offset NUM ] symhash mod NUM [ offset NUM ]
PRIMARY EXPRESSIONS
-
ether {daddr | saddr | type} -
vlan {id | cfi | pcp | type} -
arp {htype | ptype | hlen | plen | operation | saddr { ip | ether } | daddr { ip | ether } -
ip {version | hdrlength | dscp | ecn | length | id | frag-off | ttl | protocol | checksum | saddr | daddr } -
icmp {type | code | checksum | id | sequence | gateway | mtu} -
igmp {type | mrt | checksum | group} -
ip6 {version | dscp | ecn | flowlabel | length | nexthdr | hoplimit | saddr | daddr} -
icmpv6 {type | code | checksum | parameter-problem | packet-too-big | id | sequence | max-delay} -
tcp {sport | dport | sequence | ackseq | doff | reserved | flags | window | checksum | urgptr} -
udp {sport | dport | length | checksum} -
udplite {sport | dport | checksum} -
sctp {sport | dport | vtag | checksum} -
dccp {sport | dport} -
ah {nexthdr | hdrlength | reserved | spi | sequence} -
esp {spi | sequence} -
comp {nexthdr | flags | cpi} -
-
hbh {nexthdr | hdrlength} frag {nexthdr | frag-off | more-fragments | id} rt {nexthdr | hdrlength | type | seg-left} dst {nexthdr | hdrlength} mh {nexthdr | hdrlength | checksum | type} srh {flags | tag | sid | seg-left} tcp option {eol | noop | maxseg | window | sack-permitted | sack | sack0 | sack1 | sack2 | sack3 | timestamp} tcp_option_field ip option { lsrr | ra | rr | ssrr } ip_option_field # exthdr {hbh | frag | rt | dst | mh} tcp option {eol | noop | maxseg | window | sack-permitted | sack | sack0 | sack1 | sack2 | sack3 | timestamp} ip option { lsrr | ra | rr | ssrr } -
ct {state | direction | status | mark | expiration | helper | label} ct [original | reply] {l3proto | protocol | bytes | packets | avgpkt | zone | id} ct {original | reply} {proto-src | proto-dst} ct {original | reply} {ip | ip6} {saddr | daddr}
添加规则
语法:
nft {add|insert} rule [<family>] <table> <chain> [handle <handle>] <expressions> <statements> [comment <comment>]- handle:规则句柄,句柄是不变的,除非规则被删除,这就为规则提供了稳定的索引。add 添加规则到句柄规则后面,insert 添加规则到句柄规则的前面。如果省略,add 默认添加规则到链末尾,insert 默认添加规则到链的开头
- expression:负责匹配数据包
- statement:负责对匹配的数据包做后续处理
- comment:备注
expressions
expr 回调函数每处理完一条表达式,就修改 verdict 寄存器的值为 CONTINUE,继续处理下一条。
上文 expression 章节中的表达式总结的很全面,下面对常用的表达式做详细的说明:
IP

上图是 IPv4 报头图,除了最后的可选字段,其他每个字段 matches 都可以匹配,下面挑常用的介绍,后面的 ip6、tcp、udp 等等,也都是只介绍常用的,这点就不再赘述:
protocol
:上层协议 ip protocol tcp ip protocol 6 ip protocol != tcp ip protocol { icmp, esp, ah, comp, udp, udplite, tcp, dccp, sctp }saddr
:Source IP Address ip saddr 192.168.2.0/24 ip saddr != 192.168.2.0/24 ip saddr 192.168.3.1 ip daddr 192.168.3.100 ip saddr != 1.1.1.1 ip saddr 1.1.1.1 ip saddr & 0xff == 1 ip saddr & 0.0.0.255 < 0.0.0.127daddr
:Destination IP Address ip daddr 192.168.0.1 ip daddr != 192.168.0.1 ip daddr 192.168.0.1-192.168.0.250 ip daddr 10.0.0.0-10.255.255.255 ip daddr 172.16.0.0-172.31.255.255 ip daddr 192.168.3.1-192.168.4.250 ip daddr != 192.168.0.1-192.168.0.250 ip daddr { 192.168.0.1-192.168.0.250 } ip daddr { 192.168.5.1, 192.168.5.2, 192.168.5.3 }
Ip6
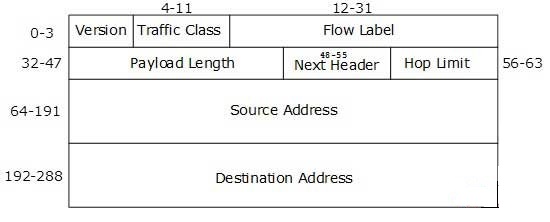
flowlabel
ip6 flowlabel 22 ip6 flowlabel != 233 ip6 flowlabel { 33, 55, 67, 88 } ip6 flowlabel { 33-55 }saddr
:Source Address ip6 saddr 1234:1234:1234:1234:1234:1234:1234:1234 ip6 saddr ::1234:1234:1234:1234:1234:1234:1234 ip6 saddr ::/64 ip6 saddr ::1 ip6 daddr ::2daddr
:Destination Address ip6 daddr 1234:1234:1234:1234:1234:1234:1234:1234 ip6 daddr != ::1234:1234:1234:1234:1234:1234:1234-1234:1234::1234:1234:1234:1234:1234
Tcp
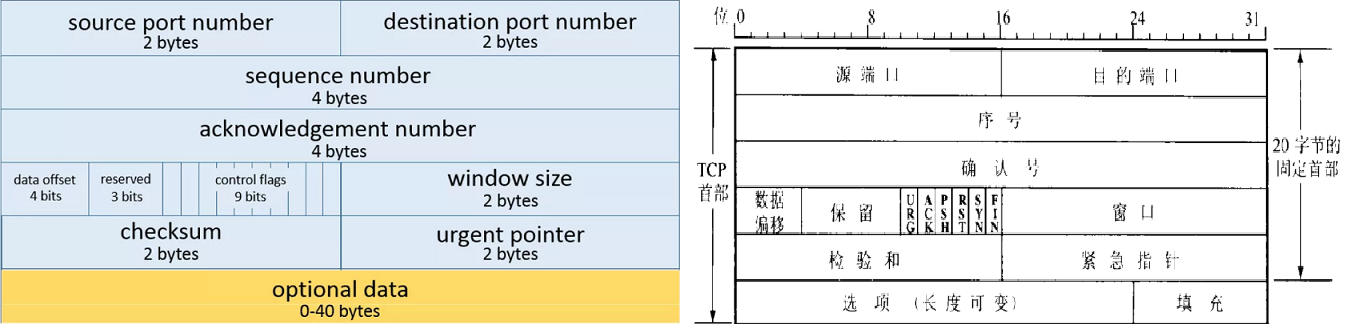
sport
:Source port tcp sport 22 tcp sport != 33-45 tcp sport { 33, 55, 67, 88} tcp sport { 33-55} tcp sport vmap { 25:accept, 28:drop } tcp sport 1024 tcp dport 22dport
:Destination port tcp dport 22 tcp dport != 33-45 tcp dport { 33-55 } tcp dport {telnet, ssh, http, https } tcp dport vmap { 22 : accept, 23 : drop } tcp dport vmap { 25:accept, 28:drop }flags
:TCP flags tcp flags { fin, syn, rst, psh, ack, urg, ecn, cwr} tcp flags cwr tcp flags != cwr
Udp
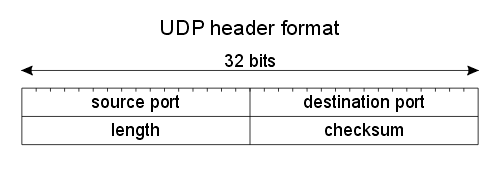
- sport
:Source port - dport
:Destination port
Udplite
Sctp
Dccp
Ah
Esp
Comp
Icmp
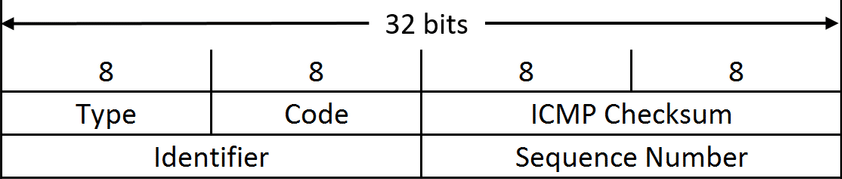
type <type>:ICMP packet type,也可以写数值,例如
icmp type echo-reply等价于icmp type 0icmp type {echo-reply, destination-unreachable, source-quench, redirect, echo-request, time-exceeded, parameter-problem, timestamp-request, timestamp-reply, info-request, info-reply, address-mask-request, address-mask-reply, router-advertisement, router-solicitation} icmp type 8 reject # 禁止别人ping我code <code>:ICMP packet code
icmp code 111 icmp code != 33-55 icmp code { 2, 4, 54, 33, 56}mtu
:ICMP packet mtu,最大传输单元 gateway
:ICMP packet gateway
Icmpv6
Ether
Dst
Frag
Hbh
Mh
Rt
Vlan
Arp
Ct
Ct 是 Conntrack 的缩写,链接跟踪
state
: State of the connection,这个匹配条件的作用和 iptables 的 state 模块一样 ct state { new, established, related, invalid,untracked } ct state != related ct state established ct state 8direction
: Direction of the packet relative to the connection,数据包相对于链接的方向 ct direction original ct direction != original ct direction {reply, original}status
:Status of the connection ct status expected ct status != expected ct status { expected,seen-reply,assured,confirmed,snat,dnat,dying }mark [set]:Mark of the connection
expiration: Connection expiration time,连接过期时间
helper “
“:Helper associated with the connection ct helper "ftp"[original|reply] bytes
ct original bytes > 100000 ct bytes > 100000[original|reply] packets
: ct reply packets < 100[original | reply] saddr
ct original saddr 192.168.0.1 ct reply saddr 192.168.0.1 ct original saddr 192.168.1.0/24 ct reply saddr 192.168.1.0/24[original | reply] daddr
ct original daddr 192.168.0.1 ct reply daddr 192.168.0.1 ct original daddr 192.168.1.0/24 ct reply daddr 192.168.1.0/24[original | reply] l3proto
ct original l3proto ipv4[original | reply] protocol
ct original protocol 6[original | reply] proto-dst
ct original proto-dst 22[original | reply] proto-src
ct reply proto-src 53
Meta
匹配(某些情况下可以 设置)数据包的元信息,虽然我现在也不知道元信息是什么?
不能省略 meta 关键字
- length – packet lenght
- protocol – packet protocol (as in skb->protocol)
- nfproto – netfilter packet protocol family (like ipv4, ipv6, etc..).
- l4proto – layer 4 protocol (tcp, udp, etc..)
- priority – packet priority, tc handle. Can be set.
- random – match against a single/simple random number
- secmark – packet secmark. Can be set.
- ibrvproto – match the bridge protocol
- ibrpvid – match the bridge pvid
可以省略 meta 关键字
- mark – packet mark. Can be set.
- iif – input interface index
- iifname – input interface name
- iiftype – input interface type
- oif – output interface index
- oifname – output interface name
- oiftype – output interface type
- skuid – socket uid
- skgid – socket gid
- nftrace – nftrace debugging bit. Can be set.
- rtclassid – realm
- ibriport – input bridge port
- obriport – output bridge port
- ibridgename – input bridge name
- obridgename – output bridge name
- pkttype – packet type. Can be set.
- cpu – cpu number
- iifgroup – input interface group
- oifgroup – output interface group
- cgroup – cgroup number
- ipsec – ipsec (secpath) packet or not
- time – packet timestamp
- day – packet timestamp
- hour – packet timestamp
Matching packets by interface name 通过接口名称匹配数据包
nft add rule filter input meta oifname lo acceptMatching packets by packet mark 通过数据标记匹配数据包
nft add rule filter output meta mark 123 counterMatching packets the socket UID 匹配套接字 UID 的数据包
nft add rule filter output meta skuid pablo counter
nft add rule filter output meta skuid 1000 counterMatching packet priority 匹配数据包的优先级
nft add rule filter forward meta priority abcd:1234
nft add rule filter forward meta priority nonestatements
语句,分为两种,终结和非终结,终结语句不会再继续处理后面的表达式和规则,防火墙完成本次任务,而非终结语句会继续处理后面的表达式或者规则。
- Verdict:重定向
- Log:记录日志并继续处理请求
- Reject:停止处理并拒绝请求
- Counter:计数
- Limit:如果达到了接收数据包的匹配限制,则根据规则处理数据包
- Nat:NAT,分为 snat 和 dnat
- Queuea:停止处理并发送数据包到用户空间程序
verdict
每条 verdict 语句都与 verdict 寄存器的预设值一一对应,只负责控制已匹配数据包的重定向,如果在决定数据包的去向之前有任何操作,交给其他类型的语句负责
expr 处理完 verdict 语句,会跳出当前表达式的循环(即上文 nftables 框架的执行流程中的循环 2)这样不管最终重定向到哪里,都会就此结束当前规则,所以 verdict 语句,要写在规则的最后。
- accept:终结语句,接受数据包
- drop:终结语句,接受数据包
- queue:将数据包排队到用户空间,queue 本身不是终结语句,但是需要搭配 accept 或者 drop 使用
- continue:跳过本条规则后面的表达式和语句,处理下一条规则
- return:
- 从一个 CHAIN 里可以 jump 到另一个 CHAIN, jump 到的那个 CHAIN 是子 CHAIN
- 从子 CHAIN return 后,回到触发 jump 的那条规则,从那条规则的下一条继续匹配
- 如果不是在子 CHAIN 里 return,而是在 main CHAIN,那么就以默认规则进行
- jump
:跳转到指定的规则链,当执行完成或者返回时,返回到调用的规则链 - goto
:类似于跳转,发送到指定规则链但不返回
log
level [over]
[burst ]:Log level log log level emerg log level alert log level crit log level err log level warn log level notice log level info log level debuggroup
[queue-threshold ] [snaplen ] [prefix “ “] log prefix aaaaa-aaaaaa group 2 snaplen 33 log group 2 queue-threshold 2 log group 2 snaplen 33
reject
with
type reject reject with icmp type host-unreachable reject with icmp type net-unreachable reject with icmp type prot-unreachable reject with icmp type port-unreachable reject with icmp type net-prohibited reject with icmp type host-prohibited reject with icmp type admin-prohibited reject with icmpv6 type no-route reject with icmpv6 type admin-prohibited reject with icmpv6 type addr-unreachable reject with icmpv6 type port-unreachable reject with icmpx type host-unreachable reject with icmpx type no-route reject with icmpx type admin-prohibited reject with icmpx type port-unreachable ip protocol tcp reject with tcp reset
counter
按照数据包的大小递增字节计数器以及包计数器的值
packets
bytes # counter 和 counter packets 0 bytes 0 是等价的,都表示从0开始计数, # 过一段时间再 nft list ruleset 查看过滤规则,packets 和 bytes 就会显示通过过滤的数据计数 counter counter packets 0 bytes 0
Limit
等同于 iptables 中的 limit 条件匹配模块
rate [over]
[burst ]:Rate limit,令牌桶算法限速 limit rate 400/minute limit rate 400/hour limit rate over 40/day limit rate over 400/week limit rate over 1023/second burst 10 packets limit rate 1025 kbytes/second limit rate 1023000 mbytes/second limit rate 1025 bytes/second burst 512 bytes limit rate 1025 kbytes/second burst 1023 kbytes limit rate 1025 mbytes/second burst 1025 kbytes limit rate 1025000 mbytes/second burst 1023 mbytes
nat
适用于 nat 链
dnat
:Destination address translation,目标地址转换 dnat 192.168.3.2 dnat ct mark map { 0x00000014 : 1.2.3.4}snat
:Source address translation 源地址转换 snat 192.168.3.2 snat 2001:838:35f:1::-2001:838:35f:2:::100masquerade [
] [to : ]:Masquerade,特殊的 snat,可以把 MASQUERADE 理解为动态的、自动化的 SNAT,如果没有动态 SNAT 的需求,没有必要使 MASQUERADE,因为 SNAT 更加高效 masquerade masquerade persistent,fully-random,random masquerade to :1024 masquerade to :1024-2048
queueaz
num
queue queue num 2 queue num 2-3 queue num 4-5 fanout bypass queue num 4-5 fanout queue num 4-5 bypass
tproxy
synproxy
flow
dup
fwd
set
map
vmap
范例
# 新建filter表
[root@centos8 ~]$nft add table ip filter
# 添加input、forward、output三个基本链,input和forward的默认策略是drop,output的默认策略是accpet
nft add chain inet filter input {type filter hook input priority 0\; policy drop\;}
nft add chain inet filter forwad {type filter hook forward priority 0\; policy drop\;}
nft add chain inet filter output {type filter hook output priority 0\; policy accept\;}
# 添加两个与TCP和UDP关联的常规链
nft add chain inet filter TCP
nft add chain inet filter UDP
# related 和 established 的流量都accept
nft add rule inet filter input ct state related,established accept
# loopback 接口流量会 accept,省略meta关键字
nft add rule inet filter input iif lo accept
# 无效的流量都 drop
nft add rule inet filter input ct state invalid drop
# 新的echo请求(ping)accept
nft add rule inet filter input ip protocol icmp icmp type echo-request ct state new accept
# 新的UDP流量跳转到UDP链
nft add rule inet filter input ip protocol udp ct state new jump UDP
# 新的TCP流量跳转到TCP链
# &:按位与;|:按位或
# fin、syn、rst、ack四个值按位或,统计有这四个值有几个为1,数据包与统计结果的flags按位与(为什么不按位或呢,因为flags有8位,其他四位不关心),如果结果只有syn位为1,就说明是tcp第一次握手
nft add rule inet filter input ip protocol tcp tcp flags \& \(fin\|syn\|rst\|ack\) == syn ct state new jump TCP
# 未由其他规则处理的所有流量会reject
nft add rule inet filter input ip protocol udp reject
nft add rule inet filter input ip protocol tcp reject with tcp reset
nft add rule inet filter input counter reject with icmp type prot-unreachable
# 由TCP和UDP链处理,打开web服务器的连接端口
nft add rule inet filter TCP tcp dport 80 accept
nft add rule inet filter TCP tcp dport 443 accept
# 允许SSH连接端口22
nft add rule inet filter TCP tcp dport 22 accept
# 允许传入DNS请求
nft add rule inet filter TCP tcp dport 53 accept
nft add rule inet filter UDP udp dport 53 accept替换规则
指定 handle,替换规则
nft replace rule [<family>] <table> <chain> handle <handle> <matches> <statements>列出规则
# 新建filter表
[root@centos8 ~]$nft add table ip filter
# 新建INPUT链
[root@centos8 ~]$nft add chain ip filter INPUT {type filter hook input priority 0\;}
# 添加规则,禁ping
[root@centos8 ~]$nft add rule ip filter INPUT icmp type 8 reject
# 列出指定链中的规则
[root@centos8 ~]$nft list chain ip filter INPUT
table ip filter {
chain INPUT {
type filter hook input priority filter; policy accept;
icmp type echo-request reject
}
}
# -a,--handle:显示句柄值;-n,--numeric:数字化输出
[root@centos8 ~]$nft -an list chain ip filter INPUT
table ip filter {
chain INPUT { # handle 4
type filter hook input priority 0; policy accept;
icmp type 8 reject # handle 6
}
}# 列出所有的规则
nft list ruleset删除规则
删除规则只能通过 handle 值,所以删除之前需要先查询规则的 handle 值
# 语法
nft delete rule [<family>] <table> <chain> handle <handle>
# 范例
[root@centos8 ~]$nft delete rule ip filter INPUT handle 7清空规则
# 清空链中的规则
nft flush chain [<family>] <table> <chain>
# 清空所有规则
nft flush ruleset数据报文分组、分类的数据结构
表与命名空间
在 nftables 中,每个表都是独立的命名空间,这就意味着不同的表中的链、集合、字典等名字可以相同。不同的应用就可以在相互不影响的情况下管理自己表中的规则,不过要注意,由于 nftables 将每个表都视为独立的防火墙,一个数据包必须被所有表中的规则放行才能真正通过,如果在一个 hook,出现两条优先级相同的链,就会进入竞争状态。
集合(sets)
集合可以用来匹配多个 IP 地址、端口号、网卡或其他任何条件。
相对 iptables 来说,nftables 原生支持集合,并不需要借助 ipset 来实现。nftables 的集合分为匿名集合与命名集合。
集合中的元素可能是连续的,也可能是不连续的,连续的使用 - 划分范围,不连续的使用 , 分割
匿名集合
范例:
nft add rule ip filter output tcp dport { 22, 23 } counter如果写在文件中,通过 -f 加载,可以使用 define 关键字定义,使用 $ 关键字调用,范例:
define CDN_EDGE = {
192.168.1.1,
192.168.1.2,
192.168.1.3,
10.0.0.0/8
}
define CDN_MONITORS = {
192.168.1.10,
192.168.1.20
}
define CDN = {
$CDN_EDGE,
$CDN_MONITORS
}
table inet filter {
chain input {
type filter hook input priority filter; policy drop;
tcp dport { http, https } ip saddr $CDN accept
udp dport { http, https } ip saddr $CDN accept
}
}命名集合
新建命名集合
add set [<family>] <table> <set> { type <type> | typeof <expression> ; [flags <flags> ;] [timeout <timeout> ;] [gc-interval <gc-interval> ;] [elements = { <element>[, ...] } ;] [size <size> ;] [policy <policy> ;] [auto-merge ;] }上文的 表达式 expression 章节介绍了 datatype 和 expression。集合中的 type 和 typeof 关键字功能类似,type 指定 datatype,typeof 指定 expression,推荐使用 typeof,更易读
type:指定集合中元素的类型,当前支持的数据类型有:
ipv4_addr : IPv4 地址
- ipv6_addr : IPv6 地址
- ether_addr : 以太网(Ethernet)地址
- inet_proto : 网络协议
- inet_service : 网络服务
- mark : 标记类型
typeof:typeof 关键字从 0.9.4 版本开始用有效,允许使用表达式(参考下文的表达式章节),让 nftables 解析基本类型
flags:标志
- constant:内容不可变
- interval:内容包含区间集
- timeout:可以给元素设置一个过期时间
timeout:设置元素的过期时间
gc-interval:
elements:给初始化的集合填充元素
size:限制集合中元素的数量
policy:集合策略
- performance [default]
- memory
auto-merge:相邻/重叠集元素自动合并(仅适用于区间集)
counter:给每个元素设置计数器
范例:
使用 @ 关键字调用命名集合
flush ruleset
table inet filter {
set ip_saddrs {
typeof ip saddr
flags interval
elements = { 10.0.0.0/24, 192.168.248.0/24 }
}
set tcp_dports {
typeof tcp dport
elements = { 22, 80, 443 }
}
chain input {
type filter hook input priority filter; policy drop;
ip saddr @ip_saddrs tcp dport @tcp_dports accept
}
}列出命名集合
# 默认列出全部集合
nft list sets [<family>]
# 列出一个集合
nft list set [<family>] <table> <set>映射(Maps)
映射的元素形式是 key-value,key 和 vaule 之间的映射关系取决于映射的 type 或者 typeof
配置文件中的语法格式:
map <map> {
type <type> : <type>
# 或
typeof <expression> : <expression>
# 或
type <type> : verdict
[flags <flags> ;]
[elements = { <element>[, ...] } ;]
[size <size> ;]
[policy <policy> ;]
}映射用于 map 和 vmap 语句,当键值均为表达式时,用于 map,当值为 verdict 语句时,用于 vmap。
map 通常用于 nat 地址转换。
- type:指定 datatype,支持以下 datatype,注意 counter 和 quota 不能用于键
- ipv4_addr : IPv4 地址
- ipv6_addr : IPv6 地址
- ether_addr : 以太网(Ethernet)地址
- inet_proto : 网络协议
- inet_service : 网络服务
- mark : 标记类型
- counter:
- quota:
- typeof:指定 expression
- flags:标志
- constant
- interval
- elements:初始化映射中的元素
- size:限制映射中元素的数量
- policy:策略
- performance [default]
- memory
范例:
使用 @ 关键字调用映射
flush ruleset
table inet filter {
set tcp_dports {
typeof tcp dport
elements = { 22, 80, 443 }
}
map test_vmap {
type ipv4_addr : verdict
flags interval
elements = {
192.168.248.0/24 : drop,
10.0.0.1/24 : accept
}
}
chain input {
type filter hook input priority filter; policy drop;
ip saddr vmap @test_vmap tcp dport @tcp_dports accept
}
}Concatenations
Metering
以前称之为 flow tables
Updating sets from the packet path
Math operations
Stateful objects
Flowtable (the fastpath network stack bypass)
脚本
可以将规则写在文件中,通过nft -f file加载。推荐这种方式
练习
说明:以下练习 INPUT 和 OUTPUT 默认策略均为 DROP
1、限制本地主机的 web 服务器在周一不允许访问;新请求的速率不能超过 100 个每秒;web 服务器包含了 admin 字符串的页面不允许访问;web 服务器仅允许响应报文离开本机
2、在工作时间,即周一到周五的 8:30-18:00,开放本机的 ftp 服务给 172.16.0.0 网络中的主机访问;数据下载请求的次数每分钟不得超过 5 个
3、开放本机的 ssh 服务给 172.16.x.1-172.16.x.100 中的主机,x 为你的学号,新请求建立的速率一分钟不得超过 2 个;仅允许响应报文通过其服务端口离开本机
4、拒绝 TCP 标志位全部为 1 及全部为 0 的报文访问本机
5、允许本机 ping 别的主机;但不开放别的主机 ping 本机
6、判断下述规则的意义